Hyperledger Network Certificates & How to Create Them
This blog represents code samples and related concepts on how to create hyperledger network certificates. These certificates will be used by peer nodes in Hyperledger Blockchain network. Crypto Config file for Generating Hyperledger Network Certificates Following is a YAML configuration file which can be used to create certificates for different network entities in the blockchain network. You can save the file with name such as crypto-config.yaml Pay attention to some of the following in above file: There are two high-level entries for organizations managing orderer node and peer nodes. They are OrdererOrgs and PeerOrgs Each org would be defined with attributes such as name, domain, specs, templates, users etc. Specs entry …
Hyperledger Fabric – Hello World with Blockchain Network
Hyperledger Fabric Hello World is about building your first blockchain network. We will make use of fabric-samples provided by Hyperledger. The first Blockchain network will be built using Docker containers. The first network will result in running containers representing some of the following: Two peer nodes each, representing two different organizations. Thus, one organization will have two peer nodes, one of which is called an anchor node and is used to ensure availability. For two organization, there will be four nodes. One node representing Ordering service Management node to do some of the following activities: Join peers to a channel Deploy and instantiate chain code Drive execution of transactions against deployed …
Docker – Shell Script to Remove Docker Images
Following script could help remove all of the docker images starting with a specific prefix. Save the script in a file namely, rmImages.sh. Change the permission using the command such as “chmod u+x rmImages.sh”. Execute the script using the command such as ./rmImages.sh. And, that is it. it would help you delete all the images starting with a specific prefix.
Docker – Script to Remove Running Containers
Following script could help remove all the running Docker containers. Save the script in a file namely, delContainers.sh. Change the permission using command such as “chmod u+x delContainers.sh”. Execute the script using the command such as ./delContainers.sh. And, that is it. it would help you delete all the containers.
Blockchain – Top Links for ICO
Following are some of top links representing the pages which provides good information on ICO (Initial Coin Offering): What is ICO? List of upcoming ICOs, token sales, past ICOs etc – ICOAlert.com Up-to-date news on ICO – Cointelegraph.com ICO Tracker from Coindesk.com Ultimate list of ICO resources from Coindesk.com
Blockchain Developers Interview Questions – Set 1
This page covers interview questions for Blockchain developers. It covers some of the following concepts in relation with Bitcoin Blockchain: Blockchain fundamentals Block related concepts [wp_quiz id=”5361″]
Kubernetes – When to use Which ServiceTypes?
Kubernetes supports different kinds of service types such as following: ClusterIP: The service of type, ClusterIP, can only be exposed to other services running within the same Kubernetes cluster. The default ServiceType is ClusterIP. NodePort: The service of type, NodePort, can be exposed externally at a static port. The service address would look like NodeIP:NodePort. External APIs can invoke the NodePort services. LoadBalancer: The service of type, LoadBalancer, can be exposed externally using cloud providers’ load balancer. ExternalName: The service of type, ExternalName, is mapped to an external name, such as helloapp.vitalflux.com.
Kubernetes – Port, Targetport and NodePort
When working with Kubernetes Service, you will come across some of the following terminologies: Port: Port is the port number which makes a service visible to other services running within the same K8s cluster. In other words, in case a service wants to invoke another service running within the same Kubernetes cluster, it will be able to do so using port specified against “port” in the service spec file. Target Port: Target port is the port on the POD where the service is running. Nodeport: Node port is the port on which the service can be accessed from external users using Kube-Proxy. Take a look at following spec defining a …
Decentralized Identity Management, Blockchain – Why Bother
This blog represents details on Decentralized Identity Management and why you should care? Given that IBM, Hyperledger has joined Blockchain Identity Consortium makes it much more important to quickly go over the concepts related with decentralized identity management. Check out a related Hyperledger project, Project Indy, on supporting independent identity on distributed ledgers. Traditional Centralized or Federated Identity Management System Conventional identity management systems have always been based on centralized authorities such as corporate directory services , certificate authorities (CA) , or domain name registries. Each of these centralized identity management systems acted as a “root of trust”. In order to have the identity management work across different systems, there is something called as federated identity management. According to Wikipedia post of …
Angular Developers Interview Questions – Quiz 1
This page represents the quiz for Angular developers who are beginning (beginners) to learn Angular. These questions can be used for interviews. [wp_quiz id=”5332″] In case you are developing web apps using Spring and Angular, check out my book, Building web apps with Spring 5 and Angular. Grab your ebook today and get started.
Configure Angular Route Definitions – Part 2
In this blog, we will learn about how to configure Angular route definitions in an Angular app by defining route definitions as a separate module at the root level. Again, this is not the most effective way of defining Angular route definitions. In third part of this series, we will learn about how to define route definitions as part of separate feature modules, and, not at the root level. In the previous blog in this series, we learned about the most trivial way of configuring route definitions in an Angular app. As the app starts getting complex, one needs to use routing concepts such as child routes, guards, resolvers, and so on. …
HBase Architecture Components for Beginners
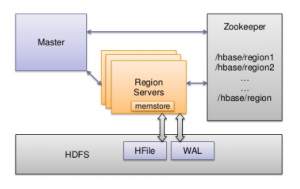
This blog represents high-level concepts on HBase architecture components. Following diagram represents the same: HBase Architecture Components – Key Building Blocks Following diagram represents the same: Pay attention to some of the following in relation to above diagram: HMaster: Responsible for coordinating the region servers including assigning regions on startup as well as recovery, and, monitoring region servers using Zookeeper Region Servers: Manages one or more regions Zookeeper: Zookeeper is used as a distributed coordination service for maintaining the server state of the cluster. Regions: Records in HBase tables are split horizontally based on the key range. Each of these splits can be called as Regions. A region contains all rows in …
Cloud Platform Trends (Oct 2017) – AWS Wins
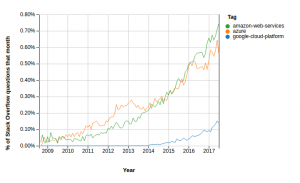
This blog represents the cloud platform trends for the month of Octobar 2017 with primary focus on AWS, Azure and Google Cloud platforms. The clear winner is AWS. Indeed.com Job Postings Trends Following represents job posting trends on the popular portal, indeed.com: Google.com Search Trends The following represents Google search trends for cloud platforms: StackOverflow Q&A Trends The following represents Stackoverflow Q&A trends for cloud platforms:
Consistent Hashing Concepts – Databases, DHT
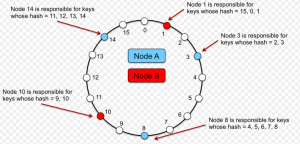
This blog represents What’s The Funda (WTF) around consistent hashing and DHT (Distributed Hash Tables), Databases use cases where it is used. Problems with Traditional Hashing Mechanism Lets understand the traditional hashing mechanism using following diagram: Pay attention to some of the following aspects as per the above diagram: Hash table/map is an array with each of the array index pointing to a linked list having each node representing a key-value pair. Keys are passed through a hash function. The index of the array (bucket) to which a specific key-value pair would get associated is a function of hash value and total size of the array. For example, in above diagram, key such as “Sam …
Deep Dive – Docker Images & Containers Internals
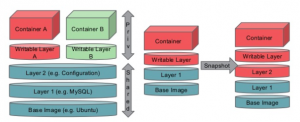
Following are some of the cool links which can help you get started with knowing Docker internals for images and containers: Docker Containers’ Filesystem Demystified Union file System for Dockers Following diagram represents the concepts on docker image and container. Pay attention to some of the following in above diagram: Docker images comprise of readable layers stacked on top of each other. These layers are shared across different containers. Each of these layers are also termed as the “image”. Thus, a docker image of any software package can comprise of multiple images (layers) such as bootfs, rootfs etc., stacked on top of each other. Following are some of the key …
Quick Glance at Kubernetes Architectural Building Blocks
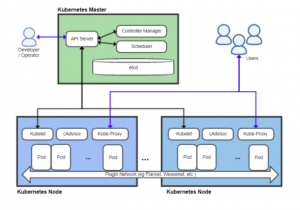
This blog represents information on some of the key architectural building blocks of Kubernetes. The greater details on Kubernetes architecture can be found on this page, Kubernetes Architecture. Following diagram represents technology architecture (with infrastructure) viewpoint of Kubernetes: Following is another viewpoint of the Kubernetes technology architecture: Pay attention to some of the following as per above diagrams: Kubernetes Master Controller Manager (kube-controller-manager): It is a daemon process that embeds the core control loops, a non-terminating loop, for regulating the state of the system. A control loop can also be seen as a controller. Details can be found on this page, kube-controller-manager. Controller manager supports different types of controllers such …
I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me