Author Archives: Ajitesh Kumar
Mathematics Topics for Machine Learning Beginners
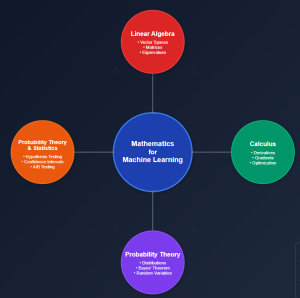
In this blog, you would get to know the essential mathematical topics you need to cover to become good at AI & machine learning. These topics are grouped under four core areas including linear algebra, calculus, multivariate calculus and probability theory & statistics. Linear Algebra Linear algebra is arguably the most important mathematical foundation for machine learning. At its core, machine learning is about manipulating large datasets, and linear algebra provides the tools to do this efficiently. Vector Spaces and Operations Matrices: Your Data’s Best Friend Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Matrix Decompositions Calculus Machine learning is fundamentally about optimization – finding the best parameters that minimize error in the loss function. …
Questions to Ask When Thinking Like a Product Leader
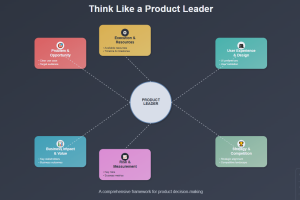
This blog represents a list of questions you can ask when thinking like a product leader. The topic includes identifying problem & opportunity, getting business impact clarity, understanding different aspects of user experience & design, success & measurement criteria, etc. If you are starting on with an exercise to solve a business problem and therefore exploring and selecting a product, you might find these questions useful. Core Problem & Opportunity Product leaders must first establish a crystal-clear understanding of the problem they’re solving and the opportunity it represents. This foundational work involves deeply understanding your target users, their pain points, and the real-world scenarios where your solution will add value. …
Three Approaches to Creating AI Agents: Code Examples
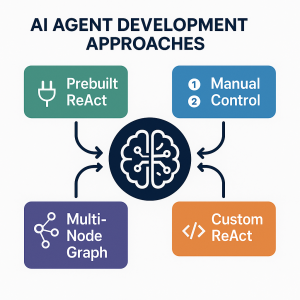
AI agents are autonomous systems combining three core components: a reasoning engine (powered by LLM), tools for external actions, and memory to maintain context. Unlike traditional AI-powered chatbots (created using DialogFlow, AWS Lex), agents can interact with end user based on planning multi-step workflows, use specialized tools, and make decisions based on previous results. In this blog, we will learn about different approaches for building agentic systems. The blog represents Python code examples to explain each of the approaches for creating AI agents. Before getting into the blog, lets quickly look at the set up code which will be basis for code used in the approaches. To explain different approaches, …
What is Embodied AI? Explained with Examples
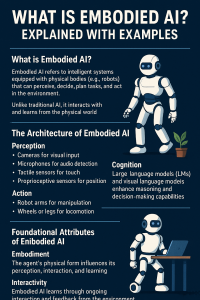
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved significantly, from its early days of symbolic reasoning to the emergence of large language models that rely on internet-scale data. Now, a new frontier is taking shape— Embodied AI that leverages Agentic AI. These systems move beyond static data processing to actively interact with and learn from the real world. Embodied AI, in particular, refers to intelligent agentic AI systems with physical presence—robots, drones, humanoids—that sense, reason, and act in physical environments. Together with Agentic AI, which emphasizes autonomy, goal-directed behavior, and decision-making over time, these developments represent a shift toward more dynamic, adaptive, and human-like forms of intelligence that integrate perception, cognition, and action. …
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) & LLM: Examples
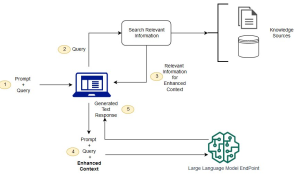
Last updated: 25th Jan, 2025 Have you ever wondered how to seamlessly integrate the vast knowledge of Large Language Models (LLMs) with the specificity of domain-specific knowledge stored in file storage, relational databases, graph databases, vector databases, etc? As the world of LLMs continues to evolve, the need for more sophisticated and contextually relevant responses from LLMs becomes paramount. Lack of contextual knowledge can result in LLM hallucination thereby producing inaccurate, unsafe, and factually incorrect responses. This is where question & context augmentation to prompts is used for contextually sensitive answer generation with LLMs, and, the retrieval-augmented generation method, comes into the picture. For data scientists and product managers keen …
How to Setup MEAN App with LangChain.js
Hey there! As I venture into building agentic MEAN apps with LangChain.js, I wanted to take a step back and revisit the core concepts of the MEAN stack. LangChain.js brings AI-powered automation and reasoning capabilities, enabling the development of agentic AI applications such as intelligent chatbots, automated customer support systems, AI-driven recommendation engines, and data analysis pipelines. Understanding how it integrates into the MEAN stack is essential for leveraging its full potential in creating these advanced applications. So, I put together this quick learning blog to share what I’ve revisited. The MEAN stack is a popular full-stack JavaScript framework that consists of MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js. Each component plays …
Build AI Chatbots for SAAS Using LLMs, RAG, Multi-Agent Frameworks

Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) providers have long relied on traditional chatbot solutions like AWS Lex and Google Dialogflow to automate customer interactions. These platforms required extensive configuration of intents, utterances, and dialog flows, which made building and maintaining chatbots complex and time-consuming. The need for manual intent classification and rule-based conversation logic often resulted in rigid and limited chatbot experiences, unable to handle dynamic user queries effectively. With the advent of generative AI, SaaS providers are increasingly adopting Large Language Models (LLMs), Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), and multi-agent frameworks such as LangChain, LangGraph, and LangSmith to create more scalable and intelligent AI-driven chatbots. This blog explores how SaaS providers can leverage these technologies …
Creating a RAG Application Using LangGraph: Example Code

Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an innovative generative AI method that combines retrieval-based search with large language models (LLMs) to enhance response accuracy and contextual relevance. Unlike traditional retrieval systems that return existing documents or generative models that rely solely on pre-trained knowledge, RAG technique dynamically integrates context as retrieved information related to query with LLM outputs. LangGraph, an advanced extension of LangChain, provides a structured workflow for developing RAG applications. This guide will walk through the process of building a RAG system using LangGraph with example implementations. Setting Up the Environment To get started, we need to install the necessary dependencies. The following commands will ensure that all required LangChain …
Building a RAG Application with LangChain: Example Code

The combination of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and powerful language models enables the development of sophisticated applications that leverage large datasets to answer questions effectively. In this blog, we will explore the steps to build an LLM RAG application using LangChain. Prerequisites Before diving into the implementation, ensure you have the required libraries installed. Execute the following command to install the necessary packages: Setting Up Environment Variables LangChain integrates with various APIs to enable tracing and embedding generation, which are crucial for debugging workflows and creating compact numerical representations of text data for efficient retrieval and processing in RAG applications. Set up the required environment variables for LangChain and OpenAI: Step …
Building an OpenAI Chatbot with LangChain

Have you ever wondered how to use OpenAI APIs to create custom chatbots? With advancements in large language models (LLMs), anyone can develop intelligent, customized chatbots tailored to specific needs. In this blog, we’ll explore how LangChain and OpenAI LLMs work together to help you build your own AI-driven chatbot from scratch. Prerequisites Before getting started, ensure you have Python (version 3.8 or later) installed and the required libraries. You can install the necessary packages using the following command: Setting Up OpenAI API Key To use OpenAI’s services, you need an API key, which you can obtain by signing up at OpenAI’s website (OpenAI) and generating a key from the …
How Indexing Works in LLM-Based RAG Applications
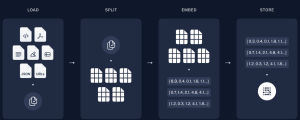
When building a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) application powered by Large Language Models (LLMs), which combine the ability to generate human-like text with advanced retrieval mechanisms for precise and contextually relevant information, effective indexing plays a pivotal role. It ensures that only the most contextually relevant data is retrieved and fed into the LLM, improving the quality and accuracy of the generated responses. This process reduces noise, optimizes token usage, and directly impacts the application’s ability to handle large datasets efficiently. RAG applications combine the generative capabilities of LLMs with information retrieval, making them ideal for tasks such as question-answering, summarization, or domain-specific problem-solving. This blog will walk you through the …
What are AI Agents? How do they work?
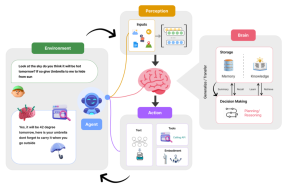
Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents have started becoming an integral part of our lives. Imagine asking your virtual assistant whether you need an umbrella tomorrow, or having it remind you of an important meeting—these agents now help us with weather forecasts, managing daily tasks, and much more. But what exactly are these AI agents, and how do they work? In this blog post, we’ll break down the inner workings of AI agents using an easy-to-understand framework. Let’s explore the key components of an AI agent and how they collaborate to enable seamless interactions, such as providing weather updates or managing tasks efficiently. What are AI Agents? AI agents are artificial entities …
Agentic AI Design Patterns Examples

In the ever-evolving landscape of agentic AI workflows and applications, understanding and leveraging design patterns is crucial for building effective and innovative solutions. Agentic AI design patterns provide structured approaches to solving complex problems. They enhance the capabilities of AI agents by enabling reasoning, planning, collaboration, and tool integration. For instance, you can think of these patterns as a blueprint for constructing a well-oiled team of specialists in a workplace—each with unique roles and tools, working in harmony to tackle a project efficiently and innovatively. Imagine a team of engineers collaborating on designing a new car, where one member focuses on aerodynamics, another on engine performance, and a third on …
List of Agentic AI Resources, Papers, Courses

In this blog, I aim to provide a comprehensive list of valuable resources for learning Agentic AI, which refers to developing intelligent systems capable of perception, autonomous decision-making, reasoning, and interaction in dynamic environments. These resources include tutorials, research papers, online courses, and practical tools to help you deepen your understanding of this emerging field. This blog will continue to be updated with relevant and popular papers periodically, based on emerging trends and the significance of newly published works in the field. Additionally, feel free to suggest any papers that you would like to see included in this list. This curated list highlights some of the most impactful and insightful …
Understanding FAR, FRR, and EER in Auth Systems

Have you ever wondered how systems determine whether to grant or deny access, and how they balance the risk of false acceptance with usability? This tutorial explores the fundamental concepts behind evaluating authentication systems or classification models using False Acceptance Rate (FAR), False Rejection Rate (FRR), and Equal Error Rate (EER). These metrics are essential for assessing the balance between usability and security in auth systems. Gaining a good understanding of these terms can greatly enhance both theoretical insights and practical application in designing reliable machine learning systems. What is False Acceptance Rate (FAR)? The False Acceptance Rate measures how frequently a system incorrectly grants access to an unauthorized individual. …
Top 10 Gartner Technology Trends for 2025

What revolutionary technologies and industries will define the future of business in 2025? As we approach this pivotal year, the technological landscape continues to evolve rapidly, reshaping industries and redefining business strategies. Gartner has unveiled its top 10 strategic technology trends for 2025, emphasizing advancements in AI, computing, and human-machine interaction. Here’s a closer look at these transformative trends: Agentic AI Agentic AI systems are designed to autonomously plan and execute tasks based on user-defined goals. These virtual assistants are poised to enhance productivity by automating decision-making processes. By 2028, Gartner predicts that at least 15% of daily work decisions will be autonomously handled by agentic AI, a significant leap …
I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me