Category Archives: Python
Pandas – Append Columns to Dataframe
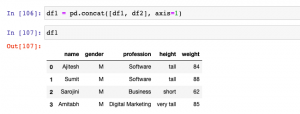
In this post, you will learn different techniques to append or add one column or multiple columns to Pandas Dataframe (Python). There are different scenarios where this could come very handy. For example, when there are two or more data frames created using different data sources, and you want to select a specific set of columns from different data frames to create one single data frame, the methods given below can be used to append or add one or more columns to create one single data frame. It will be good to know these methods as it helps in data preprocessing stage of building machine learning models. In this post, …
Pandas – Fillna method for replacing missing values
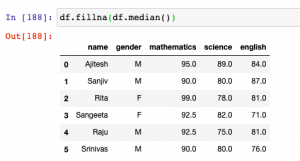
In this post, you will learn about how to use fillna method to replace or impute missing values of one or more feature column with central tendency measures in Pandas Dataframe (Python).The central tendency measures which are used to replace missing values are mean, median and mode. Here is a detailed post on how, what and when of replacing missing values with mean, median or mode. This will be helpful in the data preprocessing stage of building machine learning models. Other technique used for filling missing values is backfill or bfill and forward-fill or ffill. Before going further and learn about fillna method, here is the Pandas sample dataframe we will work with. It represents marks in …
Decision Tree Classifier Python Code Example
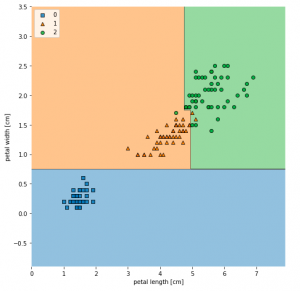
In this post, you will learn about how to train a decision tree classifier machine learning model using Python. The following points will be covered in this post: What is decision tree? Decision tree python code sample What is Decision Tree? Simply speaking, the decision tree algorithm breaks the data points into decision nodes resulting in a tree structure. The decision nodes represent the question based on which the data is split further into two or more child nodes. The tree is created until the data points at a specific child node is pure (all data belongs to one class). The criteria for creating the most optimal decision questions is …
How to Convert Sklearn Dataset to Dataframe
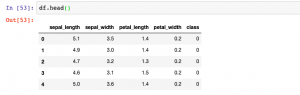
In this post, you will learn how to convert Sklearn.datasets to Pandas Dataframe. It will be useful to know this technique (code example) if you are comfortable working with Pandas Dataframe. You will be able to perform several operations faster with the dataframe. Sklearn datasets class comprises of several different types of datasets including some of the following: Iris Breast cancer Diabetes Boston Linnerud Images The code sample below is demonstrated with IRIS data set. Before looking into the code sample, recall that IRIS dataset when loaded has data in form of “data” and labels present as “target”. Executing the above code will print the following dataframe. In case, you don’t want to explicitly assign …
Sklearn SVM Classifier using LibSVM – Code Example
In this post, you learn about Sklearn LibSVM implementation used for training an SVM classifier, with code example. Here is a great guide for learning SVM classification, especially, for beginners in the field of data science/machine learning. LIBSVM is a library for Support Vector Machines (SVM) which provides an implementation for the following: C-SVC (Support Vector Classification) nu-SVC epsilon-SVR (Support Vector Regression) nu-SVR Distribution estimation (one-class SVM) In this post, you will see code examples in relation to C-SVC, and nu-SVC LIBSVM implementations. I will follow up with code examples for SVR and distribution estimation in future posts. Here are the links to their SKLearn pages for C-SVC and nu-SVC …
Python – How to Plot Learning Curves of Classifier
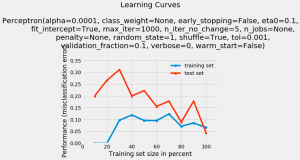
In this post, you will learn a technique using which you could plot the learning curve of a machine learning classification model. As a data scientist, you will find the Python code example very handy. In this post, the plot_learning_curves class of mlxtend.plotting module from mlxtend package is used. This package is created by Dr. Sebastian Raschka. Lets train a Perceptron model using iris data from sklearn.datasets. The accuracy of the model comes out to be 0.956 or 95.6%. Next, we will want to see how did the learning go. In order to do that, we will use plot_learning_curves class of mlxtend.plotting module. Here is a post on how to install mlxtend with Anaconda. The following …
Python – How to install mlxtend in Anaconda
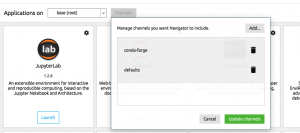
In this post, you will quickly learn about how to install mlxtend python package while you are working with Anaconda Jupyter Notebook. Mlxtend (machine learning extensions) is a Python library of useful tools for the day-to-day data science tasks. This library is created by Dr. Sebastian Raschka, an Assistant Professor of Statistics at the University of Wisconsin-Madison focusing on deep learning and machine learning research. Here is the instruction for installing within your Anaconda. Add a channel namely conda-forge by clicking on Channels button and then Add button. Open a command prompt and execute the following command: conda install mlxtend –channel Conda-forge Once installed, launch a Jupyter Notebook and try importing the following. This should work …
How to Print Unique Values in Pandas Dataframe Columns
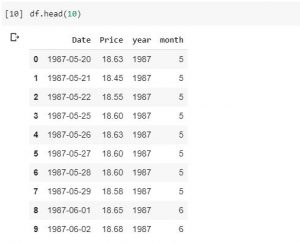
A quick post representing code sample on how to print unique values in Dataframe columns in Pandas. Here is a data frame comprising of oil prices on different dates which column such as year comprising of repeated/duplicate value of years. In the above data frame, the requirement is to print the unique value of year column. Here is the code for same. Note the method unique()
Python Quick Coding Tutorials for Experienced Developers

Learning Python has taken centerstage for many developers as Python is one of the key language for working in the field of data science/machine learning. If you are an experienced developer, this post would help you quickly get started with Python programming. In this post, you will quickly learn some of the following in relation to Python programming: Data types Input/output operations Defining functions Conditional expressions Looping constructs String functions Defining Module Defining Classes Exception handling Python Programming Concepts Data types: Python interprets and declares variables when they are equated to a value. The following represents how variables are casted to specific data types. float(variable): Casts variable to float int(variable): …
I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me