In this code, you will learn code examples, written with Python Numpy package, related to the binomial distribution. You may want to check out the post, Binomial Distribution explained with 10+ examples to get an understanding of Binomial distribution with the help of several examples. All of the examples could be tried with code samples given in this post. Here are the instructions:
Load the Numpy package: First and foremost, load the Numpy and Seaborn library
import numpy as np import seaborn as sns
Code Syntax – np.random.binomial(n, p, size=1): The code np.random.binomial(n, p, size=1) will be used to print the number of successes that will happen in one (size=1) experiment comprising of n number of trials with probability/proportion of success being p.
Tossing a Coin Example: This is an example representing 20 experiments of tossing a coin 50 times and measuring the number of successes (heads) in each of the experiments. The binomial random variable, X, in the experiment is number of successes (heads) in tossing the coins. Note that the probability that a coin appears as heads is 0.5.
np.random.binomial(50, 0.5, size=20)
The above results in an array representing a number of successes in each of the 20 experiments. Note some of the following parameters of the probability distribution:
- Mean value is 50*0.5 = 25
- Variance = 50*0.5*(1-0.5) = 12.5
- Standard deviation is Square root (12.5) = 3.53
Here is the output of the 20 experiments:
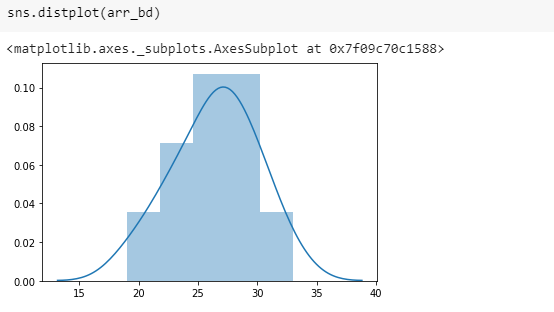
array([25, 30, 19, 24, 30, 21, 24, 33, 26, 27, 28, 27, 28, 30, 22, 26, 27,
31, 28, 23])
Here is the plot representing the outcome of the binomial experiments:
References
- Mathematics Topics for Machine Learning Beginners - July 6, 2025
- Questions to Ask When Thinking Like a Product Leader - July 3, 2025
- Three Approaches to Creating AI Agents: Code Examples - June 27, 2025
I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me