This article represents code in R programming language which could be used to create a data frame with column names. Please feel free to comment/suggest if I missed to mention one or more important points. Also, sorry for the typos.
Following are the key points described later in this article:
- Create empty dataframe with column names
- Create non-empty dataframe with column names
Create an Empty Dataframe with Column Names
Following is the code sample:
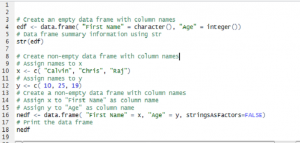
# Create an empty data frame with column names edf <- data.frame( "First Name" = character(0), "Age" = integer(0)) # Data frame summary information using str str(edf)
Following gets printed:
'data.frame': 0 obs. of 2 variables: $ First.Name: Factor w/ 0 levels: $ Age : int
Create non-empty Dataframe with Column Names
Following is the code sample:
# Assign names to x x <- c( "Calvin", "Chris", "Raj") # Assign names to y y <- c( 10, 25, 19) # Create a non-empty data frame with column names # Assign x to "First Name" as column name # Assign y to "Age" as column name nedf <- data.frame( "First Name" = x, "Age" = y) # Print the data frame nedf
Following gets printed. Note the column names such as “First Name” and “Age”
First.Name Age 1 Calvin 10 2 Chris 25 3 Raj 19
Latest posts by Ajitesh Kumar (see all)
- Three Approaches to Creating AI Agents: Code Examples - June 27, 2025
- What is Embodied AI? Explained with Examples - May 11, 2025
- Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) & LLM: Examples - February 15, 2025
I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me