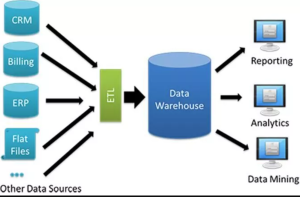
A data warehouse is a system used for reporting and data analysis, and is considered a core component of business intelligence. Data warehouses are centralized repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that can be used to answer business questions. Data warehouses are used to support business intelligence applications. Business intelligence applications are used to make decisions about the operation of the business.
A data warehouse is usually populated with data from an operational database, which contains transactions. The process of populating the data warehouse is called Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL). This process cleans, transforms, and loads the data into the data warehouse. Once the data is in the data warehouse, it can be used for reporting and analysis.
The following are some examples of data warehouses:
- Amazon Redshift
- Snowflake
- Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse
Types of Data Warehouses
The following are different types of data warehouses:
- Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW): An enterprise data warehouse provides a central repository for all the organization’s data. It contains both current and historical data. The EDW is subject-oriented, meaning that it organizes the data around subjects such as customers, products, sales, etc. An EDW is typically used by large organizations with complex needs.
- Data Mart: A data mart is a subset of an enterprise data warehouse that focuses on a specific subject area, such as sales or marketing. Data marts are usually created by departments within an organization so that they have quick and easy access to the specific information they need without having to wade through mountains of other irrelevant data.
- Operational data store (ODS): Data warehousing is a process of centralizing data from multiple sources into a single, unified data store. An operational data store (ODS) is a type of data warehouse that focuses on supporting operational applications, such as transaction processing and real-time decision making. Data in an ODS is typically refreshed on a near-real-time basis, making it more current than data in a traditional data warehouse. Data warehousing developers often use an ODS as an intermediate step in the data warehousing process, extracting data from operational systems and then staging it in the ODS before loading it into the final data warehouse. This approach can help to reduce the overall complexity of the data warehousing process and improve performance.
Data Warehouse Examples
Now that we’ve reviewed some key concepts, let’s take a look at some examples of data warehouses in action.
- Sales analysis: A company might use a data warehouse to track sales information such as sales volume, discounts offered, and customer demographics. This information could be useful for planning future marketing campaigns or analyzing which products are selling well (and which ones aren’t).
- Customer behavior analysis: A company might use a data warehouse to track customer purchase history, website usage patterns, and call center interactions. This information could be useful for understanding how customers interact with the company so that changes can be made to improve the customer experience.
- Inventory management: A company might use a data warehouse to track inventory levels, supplier information, and product demand patterns. This information could be useful for planning production schedules and ensuring that enough inventory is on hand to meet customer demand.
- Financial analysis: A company might use a data warehouse to track financial information such as budgeting details, revenue growth rates, and expense trends. This information could be useful for making strategic decisions about where to allocate resources in order to achieve financial goals.
- Marketing campaign analysis: A company might use a data warehouse to track marketing campaign performance metrics such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and cost per lead/acquisition. This information could be useful for understanding which marketing campaigns are effective at generating leads/customers and which ones are not worth the investment.
- Human resources analysis: A company might use a data warehouse to track employee information such as job titles, salary ranges, and performance reviews. This information could be useful for making decisions about hiring/firing employees and determining who deserves raises/promotions within the organization.
Conclusion
As you can see, there are many different types of data warehouses available to meet the needs of any organization, big or small. Whether you need a comprehensive solution like an enterprise data warehouse or something more focused like a virtual private data warehouse, there’s sure to be a solution out there that’s perfect for you.
- Questions to Ask When Thinking Like a Product Leader - July 3, 2025
- Three Approaches to Creating AI Agents: Code Examples - June 27, 2025
- What is Embodied AI? Explained with Examples - May 11, 2025
I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me