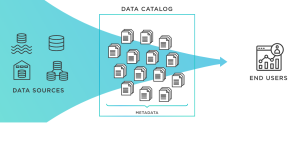
A data catalog is a comprehensive collection of information about an organization’s data assets, and it serves as the foundation for making informed decisions about how to manage and use data. This includes all types of data, structured or unstructured, spread across multiple sources including databases, websites, stored documents, and more. A good data catalog should provide users with the ability to quickly identify what types of data are available within the organization, where they are located, and who owns them. In this blog, we will learn basic concepts of data catalog along with some examples.
What is Data Catalog?
A data catalog is a comprehensive inventory of all the data sets that an organization has and makes available for use. It is essentially a collection of metadata about the various datasets, which can include details like the source of the data, connection information, data set characteristics, and security access control. The main purpose behind having a data catalog is to make it easier for users to quickly find and access the various datasets that are available within an organization.
The following are some of the motivations for having data catalog in your organization:
- Achieve data compliance
- Evangelize about data sets by leveraging data discovery aspect of data catalog
- Unify the data landscape
- Bring the business and data closer and help in enhancing data-driven culture
The functionality of a data catalog ranges from basic metadata tagging to complex features such as business glossary, data classification, data set certification, role based access control, data marketplace, querying and search functions.
- Metadata tagging is useful in quickly finding pertinent information about any particular dataset. Metadata tags provide a way for users to quickly and easily find the information they need, without having to sort through lengthy documents or databases. Metadata tags can be applied to individual files, collections of files, or entire datasets. Metadata tagging is an especially useful approach since it allows users to quickly search for specific information within a dataset by applying keywords or labels directly onto the data itself. By applying relevant metadata tags, users can easily narrow down their search results and access the information they need in a matter of seconds.
- Business glossary helps different teams communicate effectively by using standardized definitions across their respective datasets. A business glossary is an invaluable tool for helping organizations manage their data catalogs. It serves as a repository of important corporate terms, definitions, and abbreviations that are used throughout the organization. This helps ensure consistency in communication and understanding of data elements by all stakeholders. A business glossary provides a common language for data management that eliminates ambiguity and ensures everyone is using the same terminology when it comes to describing various pieces of information or datasets. By providing these shared definitions, a business glossary can help streamline processes and make it easier to compare similar datasets across different systems or departments.
- Data classification allows organizations to categorize their datasets according to specific criteria such as type of industry or geography. Data classification is an important part of the data cataloging process, as it helps to organize and store data efficiently. It allows for easier retrieval of the information later on, which can be incredibly useful when trying to find specific information within a large dataset. Data classification helps with data security, as organizations can choose which categories will require additional authentication before access is granted. This helps protect sensitive or confidential information from unauthorized users who might otherwise stumble across it accidentally. Additionally, classification helps facilitate compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA by clearly identifying what type of data is being stored, reducing the chances that an organization could accidentally violate any rules regarding how that data should be handled.
- Dataset certification ensures high quality standards by validating that any given dataset meets predetermined criteria in terms of accuracy and completeness. Data set certification ensures that all data sets are properly formatted, accurately describe their contents and adhere to the relevant standards. It helps to ensure that data sets are compliant with industry-specific regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA, which are designed to protect consumer privacy and security. By maintaining accurate and consistent records about each data set, it is easier for organizations to maintain compliance with these regulations. Data stewards play a vital role in ensuring that data set certifications are accurate and up to date, as they take responsibility for maintaining the accuracy of the data set documentation.
- Role based access control ensures that only authorized users have access to certain datasets while preventing misuse or abuse of confidential information. When it comes to data catalogs, role-based access control (RBAC) is an essential element for ensuring the security of key information. This type of access control allows organizations to determine which resources can be accessed by different users based on their roles within the organization. By using RBAC within a data catalog, companies are able to restrict user access to sensitive and confidential information such as financial or personnel records.
- Data marketplace provides users with easy access to internal, external or third-party datasets without having to make individual downloads or subscriptions each time they need them. Data marketplaces enable internal organizations / business units to quickly discover new datasets that address issues relevant to their business.
- Querying and search functions are essential for quickly locating specific datasets within an organization’s inventory.
Data Catalog Tools
Popular tools for data cataloging have been gaining in popularity lately as businesses, organizations and government agencies look for ways to better manage their data. One of the most popular tools is Alation, which combines the power of machine learning with human intelligence to help organizations understand and organize their data. Alation allows users to define a catalog of reusable terms, enabling them to quickly and easily search for information when it’s needed. It also provides a taxonomy structure that lets users group similar types of data together and tag it with relevant keywords so that it can be more easily located. Alation offers insights into how frequently certain datasets are used, helping organizations measure the value they get from specific pieces of data.
Another increasingly popular tool is Collibra, which helps make sense of complex datasets by connecting people to the right information at the right time. Collibra allows users to annotate databases with relevant context and metadata in order to facilitate discovery and collaboration between different teams within an organization. With its intuitive user interface, it enables users to build an integrated view into all available enterprise data sources, including both internal systems and external sources such as cloud services or web applications. It also makes it easier for users to find specific pieces of information by tagging them with keywords or categories. Collibra’s advanced analytics capabilities let users analyze patterns in large datasets more quickly and efficiently than ever before.
Another popular data catalog tool is Talend Data Catalog. This tool is a comprehensive solution that helps organizations easily and quickly locate, analyze, and share enterprise data assets across the organization. With Talend Data Catalog, users can discover data sources and find data sets to use for analytics or other business purposes. The tool also provides a centralized repository of information about key elements of an organization’s data landscape so that users can access relevant meta-data and have insights into how different stakeholders in the company use their data. Not only this, but it also helps in detecting sensitive content within organizational systems, as well as providing insights on trustworthiness of services used to store and process this important corporate asset.
Another popular data catalog tool is IBM’s Watson Knowledge Catalog. IBM’s Watson Knowledge Catalog is another useful tool when it comes to organizing large amounts of data within an organization. This tool allows users to quickly identify documents among massive datasets through machine-learning algorithms and natural language processing technology that can detect patterns among terms used in documents related to certain topics or keywords searched by the user. It makes finding relevant information much faster than manually going through each document one by one while also allowing users to customize searches based on personal preferences like date range or file type so they can narrow down results even further when needed.
Data Catalog Cloud-based Tools
One of the most popular cloud tools for data cataloging today is Google Cloud Data Catalog. This powerful tool provides users with an automated way to discover, manage, and understand their data, as well as to provide secure sharing capabilities. It allows organizations to easily find and access data from across multiple storage systems and databases, including BigQuery, Cloud Storage, Cloud SQL, and more. With its in-depth search capabilities and detailed visualizations, Google Cloud Data Catalog enables users to quickly identify the right information they need.
Other popular tools for data cataloging include Amazon Web Services (AWS) Glue Data Catalog and Microsoft Azure Data Catalog. AWS Glue Data Catalog is a fully managed metadata repository that provides customers with a unified view of their data in the cloud. With this service, customers can store table and structure definitions for various sources of stored data in the cloud or on-premises. Furthermore, customers can use AWS Glue Data Catalog to classify as well as discover datasets stored in various formats such as Amazon S3 buckets or other databases like Apache Hive or Apache Cassandra.
Microsoft Azure Data Catalog is another powerful tool that helps organizations organize their large amounts of data stored in the cloud. This tool makes it easy for organizations to gain insights into their huge volumes of structured and unstructured data by providing them with tools like AI-driven smart search capabilities and filters that allow users to quickly locate exactly what they are looking for. Additionally, Microsoft Azure Data Catalog allows users to tag their datasets with custom metadata fields so they can easily locate them later on.
Conclusion
Data Catalogs are powerful tools for product managers, data scientists and architects alike when it comes to managing large amounts of organizational information efficiently and effectively. By providing an organized overview of all available datasets within an organization—including their location and ownership status—data catalogs make it much easier for users to find relevant information quickly without wasting time searching through multiple folders or documents manually. Additionally, by tracking the lifecycle status of each dataset, organizations can better ensure compliance with industry regulations while reducing risk associated with mishandling personal information contained within their datasets. Finally, a comprehensive view into an organization’s usage patterns helps inform decisions about resource allocation across initiatives so that time and money are spent wisely on projects that have the highest potential impact on success.
- The Watermelon Effect: When Green Metrics Lie - January 25, 2026
- Coefficient of Variation in Regression Modelling: Example - November 9, 2025
- Chunking Strategies for RAG with Examples - November 2, 2025

how to collect catalog data?