In this post, you will learn about some of the 5 most popular or useful set of unary universal functions (ufuncs) provided by Python Numpy library. As data scientists, it will be useful to learn these unary functions by heart as it will help in performing arithmetic operations on sequential-like objects. These functions can also be termed as vectorized wrapper functions which are used to perform element-wise operations.
The following represents different set of popular functions:
- Basic arithmetic operations
- Summary statistics
- Sorting
- Minimum / maximum
- Array equality
Basic Arithmetic Operations
The following are some of the unary functions whichc an be used to perform arithmetic operations:
- add, subtract, multiply, divide, exp
- add.reduce
- sum
Here is the sample code demonstrating the usage of the above functions:
import numpy as np
#
# Create an array of 5 numbers between 5 and 10
#
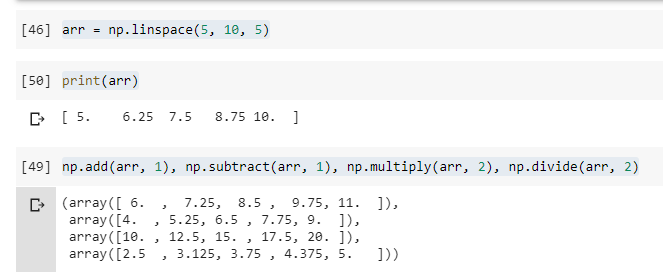
arr = np.linspace(5, 10, 5)
#
# Print array
#
print(arr)
#
# Perform arithmetic operations
#
np.add(arr, 1), np.subtract(arr, 1), np.multiply(arr, 2), np.divide(arr, 2)
Here is how the output would look like:
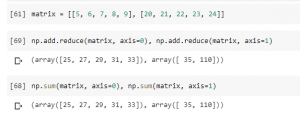
In case, you want to add all the numbers in a row or column and get the output as matrix, functions such as add.reduce or sum is used with axis. In the code sample given below, a 2 x 5 matrix is reduced by rows (axis=1) and columns (axis=0)

Summary Statistics
The following are some of the methods which can be used for calculating summary statistics:
- mean, median: Finds the mean and median of the data sample respectively.
- std: Finds the standard deviation of the data
- var: Finds the variance of the data
Here is the code demonstrating the usage of above functions with SKlearn IRIS dataset.
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
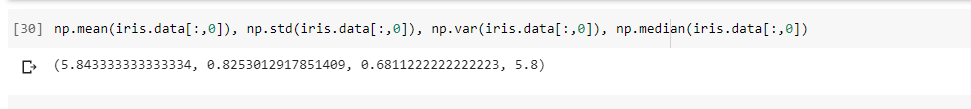
np.mean(iris.data[:,0]), np.std(iris.data[:,0]), np.var(iris.data[:,0]), np.median(iris.data[:,0])
Here is how the output will look like:
Sorting
The following represents the Numpy unary functions which can be used for sorting the array:
- sort: Sort the data
- argsort: Finds the indices of the sorted data
Here is the code demonstrating the usage of above functions with SKlearn IRIS dataset:
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
iris.data[0:10, 0]
np.sort(iris.data[0:10, 0])
np.argsort(iris.data[0:10, 0])
Here is how the output will look like:

Finding Maximum / Minimum
The following are some of the methods which can be used for finding maximum and minimum value from a data array:
- min: Finds the minimum of the array
- max: Finds the maximum of the array
- argmin: Finds the index of the minimum of the array
- argmax: Finds the index of the maximum of the array
Here is the code demonstrating the usage of above functions with SKlearn IRIS dataset:
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
iris.data[0:10, 0]
np.min(iris.data[0:10, 0]), np.argmin(iris.data[0:10, 0])
np.max(iris.data[0:10, 0]), np.argmax(iris.data[0:10, 0])
Here is how the output will look like:

- The Watermelon Effect: When Green Metrics Lie - January 25, 2026
- Coefficient of Variation in Regression Modelling: Example - November 9, 2025
- Chunking Strategies for RAG with Examples - November 2, 2025

I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me