Google’s breakthrough research in machine learning and responsible AI has culminated in the development of their next-generation large language model (LLM), PaLM 2. This model represents a significant evolution in natural language processing (NLP) technology, with the capability to perform a broad array of advanced reasoning tasks, including code and math, text classification and question answering, language translation, and natural language generation.
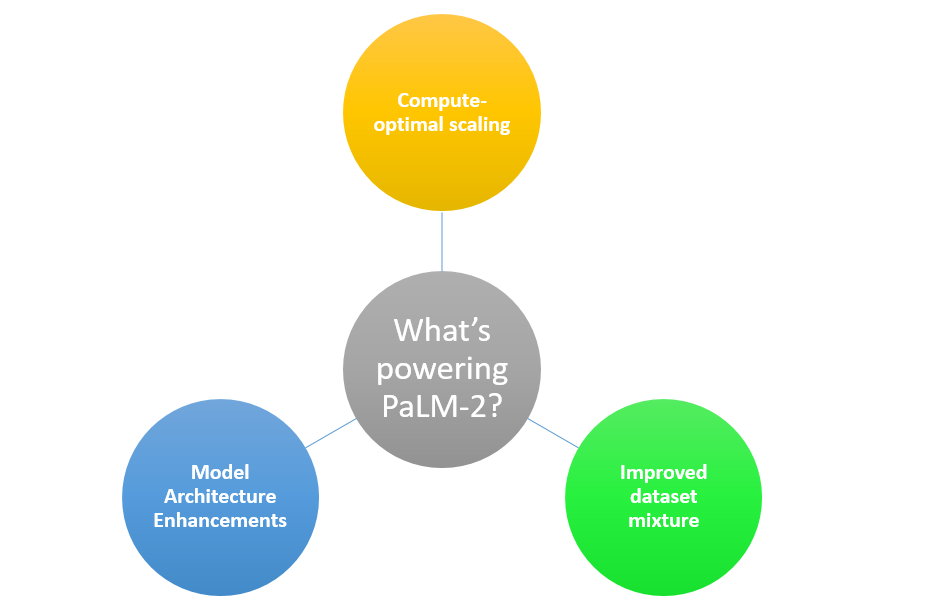
The unique combination of compute-optimal scaling, an improved dataset mixture, and model architecture enhancements is what powers PaLM 2’s exceptional capabilities. This combination allows the model to achieve superior performance than its predecessors, including the original PaLM, across all tasks.
PaLM 2 was built with Google’s commitment to responsible AI development and safety at its core. The model was rigorously assessed for potential harms and biases, as well as its capabilities and downstream uses in both research and in-product applications. Its applications extend to other state-of-the-art models like Med-PaLM 2 and Sec-PaLM, and it fuels Google’s generative AI features and tools, such as Bard and the PaLM API.
The capabilities of PaLM 2 are as diverse as they are impressive. The model exhibits some of the following:
- Superior reasoning skills, with the ability to decompose complex tasks into simpler subtasks and an enhanced understanding of human language nuances.
- Its multilingual proficiency is also remarkable, thanks to its pre-training on parallel multilingual text and a significantly larger corpus of various languages than its predecessor.
- Excels at coding, having been pre-trained on a large quantity of webpage, source code, and other datasets. This training enables it to generate specialized code in several programming languages, including Python, JavaScript, Prolog, Fortran, and Verilog
The performance of PaLM-2 model has been validated on a range of benchmarks and has demonstrated improved multilingual toxicity classification capabilities and built-in control over toxic generation. The model continues Google’s commitment to safety in AI development, with thorough evaluations for potential harms and bias in a range of downstream usesz.
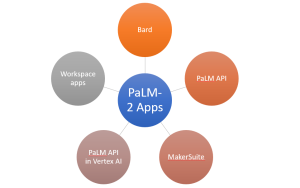
PaLM 2 is already powering a suite of generative AI features at Google.
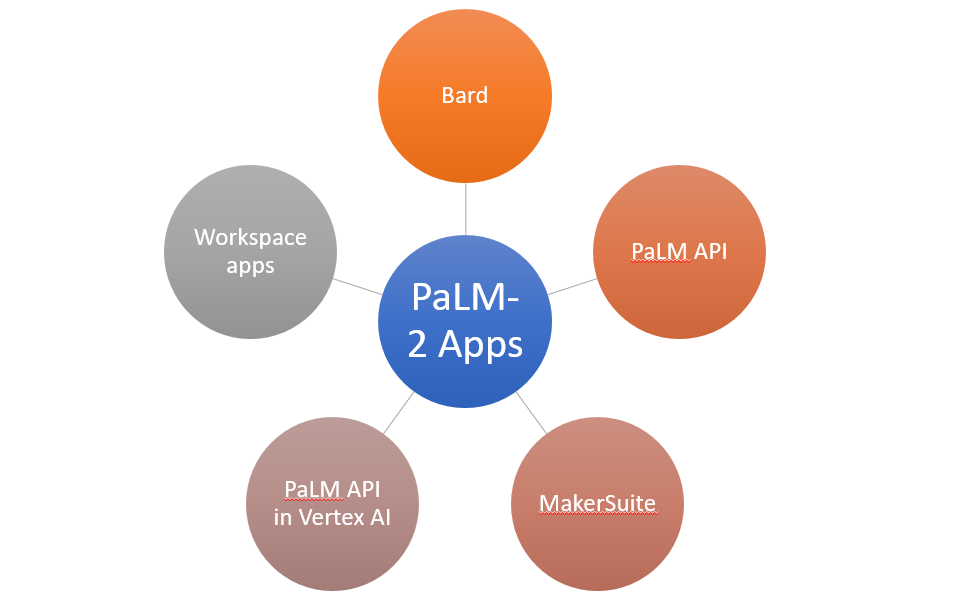
- Among these are Bard, a creative collaborator for users;
- The PaLM API, which allows developers to build generative AI applications;
- MakerSuite, a tool for prototyping generative AI ideas; and
- The PaLM API in Vertex AI, for developing generative AI applications.
- Driving generative AI features in Workspace, such as email summarization in Gmail and brainstorming and rewriting in Docs
As Google’s latest advancement in AI, PaLM 2 is poised to revolutionize the way we interact with language technology, paving the way for more nuanced, creative, and efficient communication.
- The Watermelon Effect: When Green Metrics Lie - January 25, 2026
- Coefficient of Variation in Regression Modelling: Example - November 9, 2025
- Chunking Strategies for RAG with Examples - November 2, 2025

I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me