This post represents best practices in relation to storing documents or files in the Blockchain. The need to determine best practices arises from the fact that business between two or more parties ends up exchanging documents consisting of data related to the agreement, business details etc. One often questions whether one store’s document or file in the blockchain or the hash of the document/file in the Blockchain.
Store documents in Blockchain – Best Practice/Recommendation
As a best practice, it is not recommended to store the document (PDF format or otherwise) or file in the Blockchain. Different blockchain frameworks limit the size of the block which can be added to the blockchain. Although in blockchain network such as Ethereum, there is theoretically no limit for the block size, blockchain is inherently not meant for data storage because storing large documents will turn out to be computationally very expensive. That said, there are blockchain-like solutions such as Storj which have been designed to store data.
On the other hand, it is recommended to take the hash of the document and store the hash value as part of a transaction within a block in the blockchain. The following diagram represents the same.
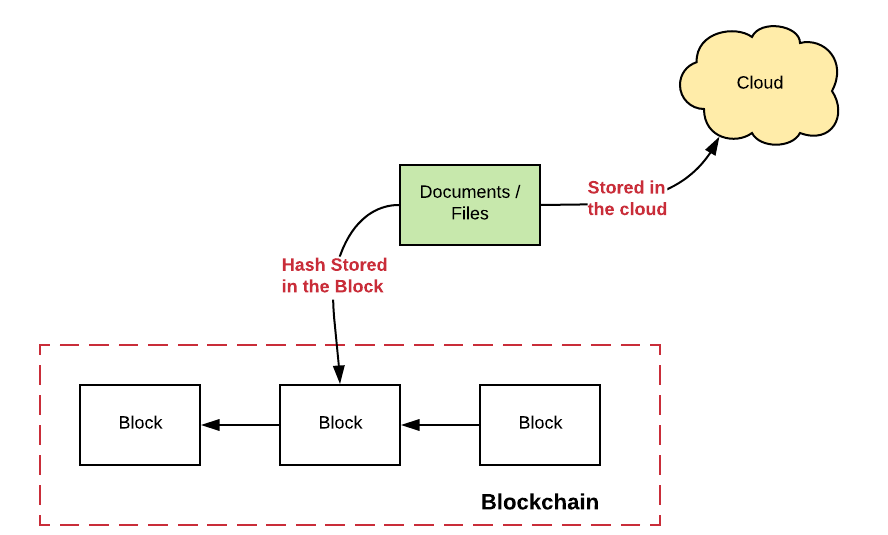
Fig 1. Store Documents or Files in Blockchain Network
The hash value of the document is of fixed length. If hashed with SHA-256, it is a string of 64 HEX characters (32 bytes). It is important to note that along with hash value, the timestamp of when the document is created, also gets recorded in the Blockchain. The authenticity of the document can later be verified by interested parties by taking the hash of the document and matching the hash value with the hash value stored in the Blockchain.
What are benefits of storing the hash of documents in the Blockchain?
The benefits of the above approach are some of the following:
-
Brings the general benefit of the Blockchain in relation to the document, such as integrity, non-repudiation, authentication etc.
-
Store Document related information: As part of the transaction, information such as who created the document, version, timestamp etc also gets recorded.
-
Minimize the fraud: In case the document is changed, the hash value won’t match with the hash value (of the original document) stored in the blockchain.
-
Document history using the timestamp: The change history of a particular document vis-a-vis the date/time on which it got changed gets recorded as the digital timestamp.
- The Watermelon Effect: When Green Metrics Lie - January 25, 2026
- Coefficient of Variation in Regression Modelling: Example - November 9, 2025
- Chunking Strategies for RAG with Examples - November 2, 2025

I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me