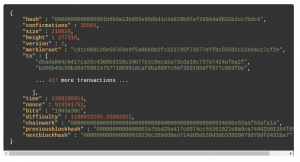
This blog represents a sample bitcoin block of a Bitcoin Blockchain. Read greater details from this Oreilly book, Mastering Bitcoin.
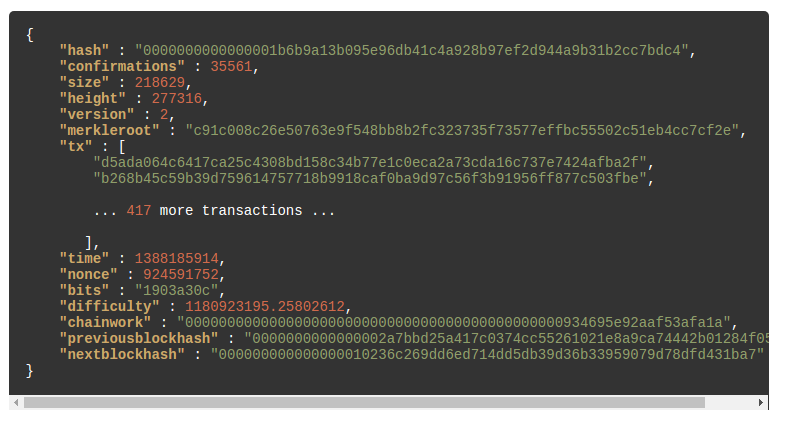
Figure 1. Sample bitcoin block
Pay attention to some of the following:
- Block file format: The block is represented as a file in JSON format
- Merkle root: Merkle root represents the hash of the root of merkle tree created as a result of combining hash of children nodes. Leaf of the merkle tree represents the hash of the transaction. It takes up 32 bytes of storage. It forms part of Block header.
- Time: Timestamp when the block is created. It takes up 4 bytes of storage. Forms part of block header.
- Difficulty: Represents difficult target and takes up 4 bytes of storage. Forms part of block header.
- Nonce: Counter which helped achieve the difficulty target. Takes up 4 bytes of storage and forms part of block header.
- Previousblockhash: Represents hash of the previous block. Takes up 32 bytes and forms part of the block header.
- Height: Height of the block
- Size: Size of the block
- Tx: List of hash values of the transactions included in the block.
- Hash: Block identifier. It is created as a function of block header.
Latest posts by Ajitesh Kumar (see all)
- Mathematics Topics for Machine Learning Beginners - July 6, 2025
- Questions to Ask When Thinking Like a Product Leader - July 3, 2025
- Three Approaches to Creating AI Agents: Code Examples - June 27, 2025
I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me