The diagram below represents application communication viewpoint at key building blocks of Hyperledger Fabric 1.0 architecture:
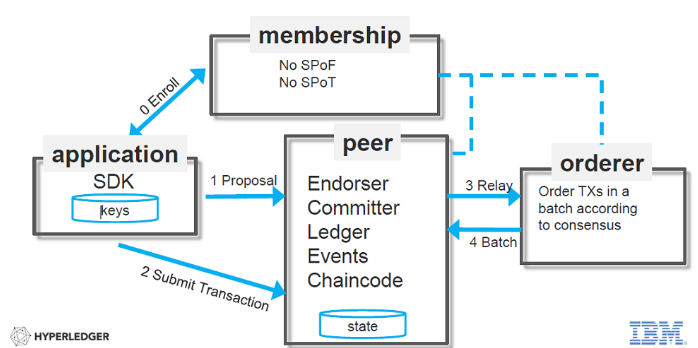
Figure 1. hyperledger fabric 1.0 architecture
Following are some of the key building blocks of Hyperledger Fabric 1.0 Architecture:
- Membership Services Provider: Enrolls the clients
- Peers: Peer nodes can be endorser (endorse proposal for transaction)and committer nodes (write block of transactions to ledger)
- Chaincode: Smart contract written in Java/Go which is invoked by a transaction. Peer nodes having chaincode becomes the endorser for that chaincode. ESCC (Endorser system chain code) executes the chaincode using proposal and read-write set information.
- Ledger: Ledger which holds the copy of transactions in form of blocks
- Ordering service: Consenter service which validates the transaction using VSCC (Validation system chaincode), orders the transaction in a block and sends it to peer nodes (endorsers & committers)
Latest posts by Ajitesh Kumar (see all)
- The Watermelon Effect: When Green Metrics Lie - January 25, 2026
- Coefficient of Variation in Regression Modelling: Example - November 9, 2025
- Chunking Strategies for RAG with Examples - November 2, 2025

I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me