- What is a binary search tree?
- What are different kind of traversals?
- Code Samples
What is a binary search tree?
A binary search tree is a binary tree in which every node contains a key that satisfies following criteria:
- The key in left child is less than the key in the parent node
- The key in the right child is more than the parent node
- The left and right child are again binary search trees.
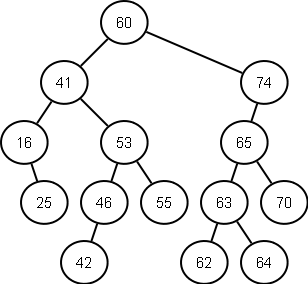
Following diagram represents a binary search tree:
What are different kind of traversals?
Following are three different kind of traversals:
- Preorder traversal: In preorder traversal, the node is visted first and then, left and right sub-trees.
- Inorder traversal: In inorder traversal, the node is visited between left and right sub-tree.
- Postorder traversal: In postorder traversal, the node is visited after left and right subtrees.
Code Sample – How to Create a Binary Search Tree
If the numbers such as {20, 15, 200, 25, -5, 0, 100, 20, 12, 126, 1000, -150} are to be stored in a BinaryTree (represented by code below), following would get printed using different kind of traversal mechanism:
//Preorder traversal
20, 15, -5, -150, 0, 12, 200, 25, 20, 100, 126, 1000
// Inorder traversal
-150, -5, 0, 12, 15, 20, 20, 25, 100, 126, 200, 1000
//Postorder traversal
-150, 12, 0, -5, 15, 20, 126, 100, 25, 1000, 200, 20
Following is the code for creating binary tree that uses following BinaryTree class and traversals:
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree( 20 );
int[] nums = {15, 200, 25, -5, 0, 100, 20, 12, 126, 1000, -150};
for(int i : nums ) {
tree.addNode( i );
}
tree.traversePreOrder();
tree.traverseInOrder();
tree.traversePostOrder();
Following is the code for BinaryTree class:
public class BinaryTree {
private int data;
private BinaryTree left;
private BinaryTree right;
public BinaryTree(int num) {
this.data = num;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
// As a convention, if the key to be inserted is less than the key of root node, then key is inserted in
// left sub-tree; If key is greater, it is inserted in right sub-tree. If it is equal, as a convention, it
// is inserted in right sub-tree
public void addNode(int num) {
if (num < this.data) {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.addNode(num);
} else {
this.left = new BinaryTree(num);
}
} else {
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.addNode(num);
} else {
this.right = new BinaryTree(num);
}
}
}
// Visit the node first, then left and right sub-trees
public void traversePreOrder() {
System.out.println( this.data );
if( this.left != null ) {
this.left.traversePreOrder();
}
if( this.right != null ) {
this.right.traversePreOrder();
}
}
// Visit left sub-tree, then node and then, right sub-tree
public void traverseInOrder() {
if( this.left != null ) {
this.left.traverseInOrder();
}
System.out.println( this.data );
if( this.right != null ) {
this.right.traverseInOrder();
}
}
// Visit left sub-tree, then right sub-tree and then the node
public void traversePostOrder() {
if( this.left != null ) {
this.left.traversePostOrder();
}
if( this.right != null ) {
this.right.traversePostOrder();
}
System.out.println( this.data );
}
}
- The Watermelon Effect: When Green Metrics Lie - January 25, 2026
- Coefficient of Variation in Regression Modelling: Example - November 9, 2025
- Chunking Strategies for RAG with Examples - November 2, 2025

I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me