This article represents practice test and revision notes on Introduction to Hyperledger Fabric. These questions and answers can prove to be very helpful to check your knowledge of Hyperledger Fabric if you are appearing for Hyperledger Fabric interview in near future.
Hyperledger Fabric is an open-source framework for building distributed ledger solutions. The unique thing about Hyperledger Fabric is that it supports pluggable implementations of different components such as identity management, consensus algorithm etc.
Revision notes on Introduction to Hyperledger Fabric
- Hyperledger Fabric can be used for creating private and permissionless Blockchain network.
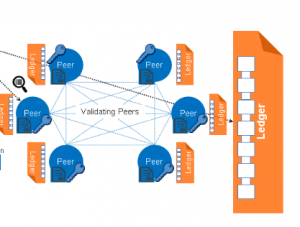
- Blockchain Participants – Membership
- Members join Hyperledger Fabric Blockchain network using Membership Service Provider (MSP) service.
- Hyperledger Fabric allows custom MSP to be plugged.
- Distributed Ledger – Data and Database
- Hyperledger Fabric allows ledger data to be stored in multiple different formats.
- Hyperledger Fabric distributed ledger is a combination of world state database and transaction logs.
- Hyperledger Fabric allows ledger data to be stored in following subsystems:
- The key-value database such as LevelDB/CouchDB for storing the state of the ledger. This is also called as world state.
- Logs storing transaction logs having transaction details.
- Hyperledger Fabric distributed ledger is a combination of world state database and transaction logs.
- Channels
- Hyperledger Fabric allows two or more participants to create a private channel for creating and maintaining the separate ledger of transactions. This ledger is not visible to anyone else than the member participating in the channel.
- A participant can belong to multiple Hyperledger Fabric blockchain networks through channels.
- Smart Contract
- Hyperledger Fabric smart contracts are called as chaincode.
- External applications need to invoke chaincode to interact with ledger.
- The following represents a different kind of chaincode:
- System chaincode: Defines operating parameters for the channel
- Lifecycle and configuration chaincode: Defines rules for the channel
- Endorsement and validation system chaincode: Defines requirements for endorsing and validating the transactions.
- Consensus
- Hyperledger Fabric allows custom consensus algorithm to be plugged.
- Transactions must be written to the distributed ledger in the order in which they occur
Practice Test on Introduction to Hyperledger Fabric
[wp_quiz id=”6159″]
References
- The Watermelon Effect: When Green Metrics Lie - January 25, 2026
- Coefficient of Variation in Regression Modelling: Example - November 9, 2025
- Chunking Strategies for RAG with Examples - November 2, 2025

I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me