This post represents my thoughts on why you should take the Google Machine Learning (ML) Crash Course. Most importantly, this course would benefit both the beginners and also the intermediate level data scientists/machine learning researchers. Each of the topics is covered as with videos, reading text and programming exercises. You learn some of the following as part of doing the course:
- ML concepts which help learn concepts related to building machine learning models such as training/validating/testing the models, feature engineering, model overfitting, regularization techniques to penalize complex models, neural networks etc.
- ML engineering concepts which help learn different aspects of machine learning system such as ML systems components, offline/online training, offline/online prediction, and data dependencies.
- ML real-world examples cover examples related to cancer prediction, 18th-century literature etc, and also presents the effective ML guidelines.
ML Concepts Overview
The ML concepts cover almost all important topics which would help one refresh ML concepts:
- Linear regression techniques
- Classification learning algorithms including logistic regression
- Aspects of machine learning such as training, validation, and testing of ML models. The following are some related pages:
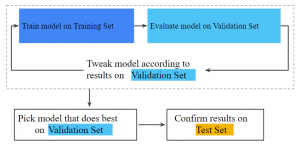
Here is a diagram obtained from one of the pages which represent clarity on ML model training, validation and test data split:
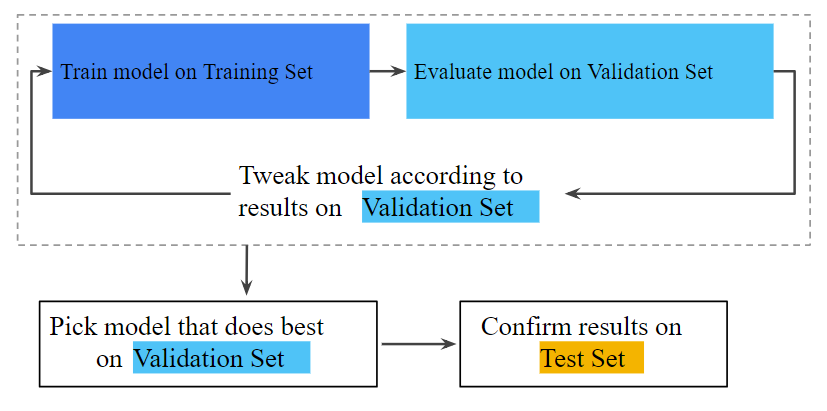
Fig: ML model learning phases: training, validation, testing
- Loss function such as gradient descent and stochastic gradient descent. The following are some cool pages:
- Model overfitting and bias
- Feature engineering, qualities of good features. In addition, topics such as feature crosses, one-hot-encoding is described with examples.
- The concept of regularization including L1, L2 regularization for dealing with model overfitting; Here is a diagram which is used to represent model overfitting. And, the problem gets solved by penalizing the complex models using regularization concept which is discussed in detail.
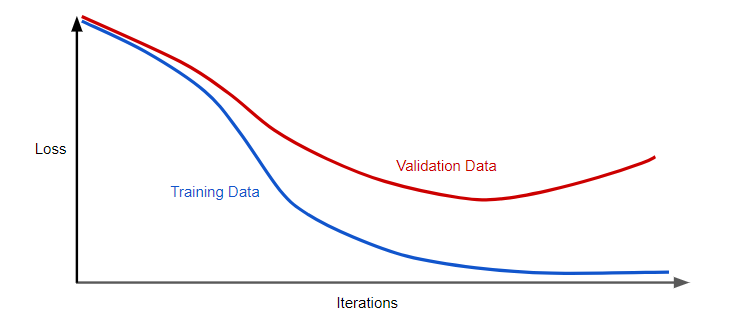
Fig: Generalization Curve
- Evaluation metrics such as precision, recall, ROC and AUC for assessing the model.
- Introduction to neural networks, training neural networks, multi-class neural networks
ML Engineering Concepts
The following are different topics which are covered as part of ML engineering concepts:
- ML systems components: The following components are covered:
- Data/feature processing (data extraction, data verification, feature extraction)
- Data analysis
- ML code
- Monitoring
- Configuration
The following diagram represents the above:
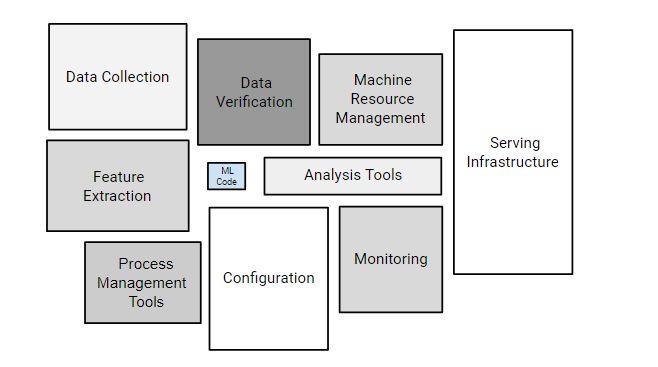
Fig: ML systems components
- Offline (Static) vs Online (Dynamic) training: Static and dynamic model concepts are discussed. Static models are trained offline in the batch manner once in a while, and dynamic models are trained online with production data continually entering into the system and getting used for training the models. It also discusses the subtle aspects of offline vs online training vis-a-vis care one has to take in both the cases to avoid model performance from degrading.
- Offline (Static) vs Online (Dynamic) inference/prediction: Static vs dynamic inference/predictions is discussed. Static inference represents predictions made as part of a batch process ran at regular intervals while online or dynamic predictions are done in the real time. There are advantages and disadvantages to doing both and same is discussed.
- Data dependencies: Some of the following aspects of data that impact the model performance are discussed.
- Reliability
- Versioning
- Correlation
- Necessity
- Feedback loops
ML Real-world Examples
This acts as an icing on the cake. The following are some of the examples covered in this section:
- Cancer prediction model: Model is built to predict the cancer disease in a patient. The example depicted what went wrong with training/testing when the prediction on new data went terribly wrong.
- 18th-century literature model: A model was built to predict the author political affiliation. The points such as what needs to be paid attention to while deciding on training/validation/test data split.
- Some of the most important ML effective guidelines were also discussed such as starting with a simple model, focusing on ML model pipeline correctness, monitoring the features, review the model performance etc.
References
Summary
In this post, you learned about details covered in the Google Machine Learning Crash course. To summarize, you would be able to learn ML concepts, ML engineering topics (data dependencies, static vs dynamic training and inferences) and some real-world examples such as cancer prediction etc.
- The Watermelon Effect: When Green Metrics Lie - January 25, 2026
- Coefficient of Variation in Regression Modelling: Example - November 9, 2025
- Chunking Strategies for RAG with Examples - November 2, 2025

I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me