This blog represents steps required to enable replication in MongoDB when access control is disabled. The related details can be found on the page, Deploy Replica Set.
Following are some of the key aspects which need to be understood in relation with MongoDB replica set:
- MongoDB replicaset consists of odd number of servers. This is done to achieve quorum in order to select a master server when one of the existing master server does down.
Following are some of the steps which needed to be done to enable replication with MongoDB:
- Check MongoDB replication status
- Install additional Mongodb instances
- Start each member of replica set
- Initiate the Replica set
- Add members to the replica set
- Validate that replication works
Check MongoDB Replication Status
First and foremost, lets check the replication status of MongoDB instance. Grant the clusterAdmin role to the admin user, if not present. Following command grants the clusterAdmin role to admin user. Before executing following command, make sure you have selected the admin database by executing command such as use admin and login into the admin database using command such as db.auth(“admin”, “adminPassword”).
db.grantRolesToUser("admin", ["clusterAdmin"]);
Once done with above, execute one of the following commands to get information in relation with replication:
rs.conf();
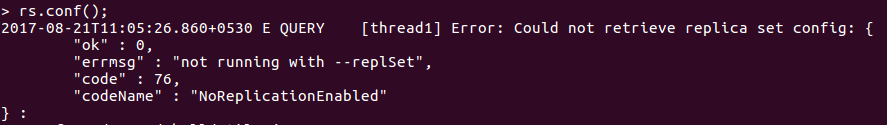
Figure 1. MongoDB Replication Not Enabled
db.runCommand({replSetGetConfig: 1});
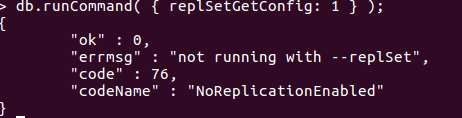
Figure 2. MongoDB Replication Not Enabled based on replSetGetConfig command
Observe that replication is not yet enabled.
Install Additional Mongodb instances
Install two additional mongodb instances on, maybe, another VMs. One can also try with docker containers.
Start each member of replica set
Start each member of the replica set by specifying the name of the replicaset using –replSet option. Following is sample command:
sudo mongod --dbpath /path/to/mongo/data --replSet "vflux01"
Make sure the name of replica set is same. In above command, –dbpath is used to specify the path of mongo data directory. The value can be found from /etc/mongod.conf.
Initiate the Replica set
Connect to one of the member of the replica set and execute following command, given name of the replicaSet is set to “vflux01”:
rs.initiate( {
_id : "vflux01",
members: [ { _id : 0, host : "ip_address_of_current_mongo_instance:27017" } ]
})
Note that rs.initiate command only needs to be executed on one and only one member of the replica set. Execute following commands to make sure replica set is configured correctly.
rs.conf()
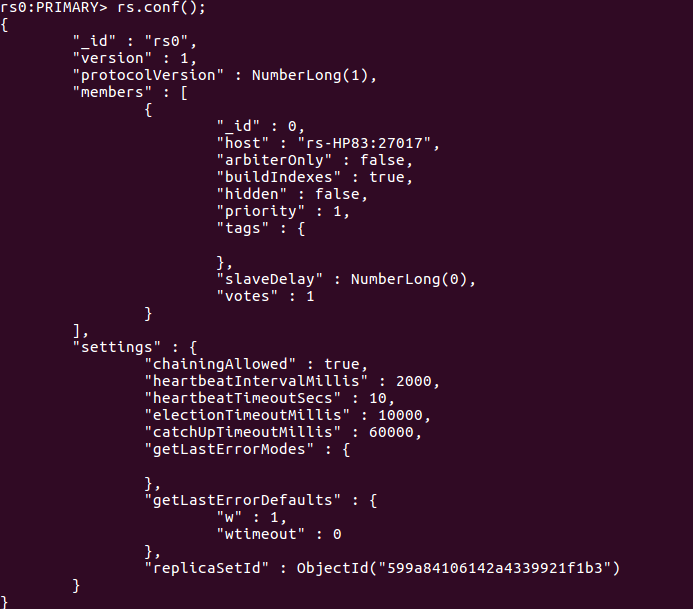
Figure 3. MongoDB Replication Enabled
rs.status()
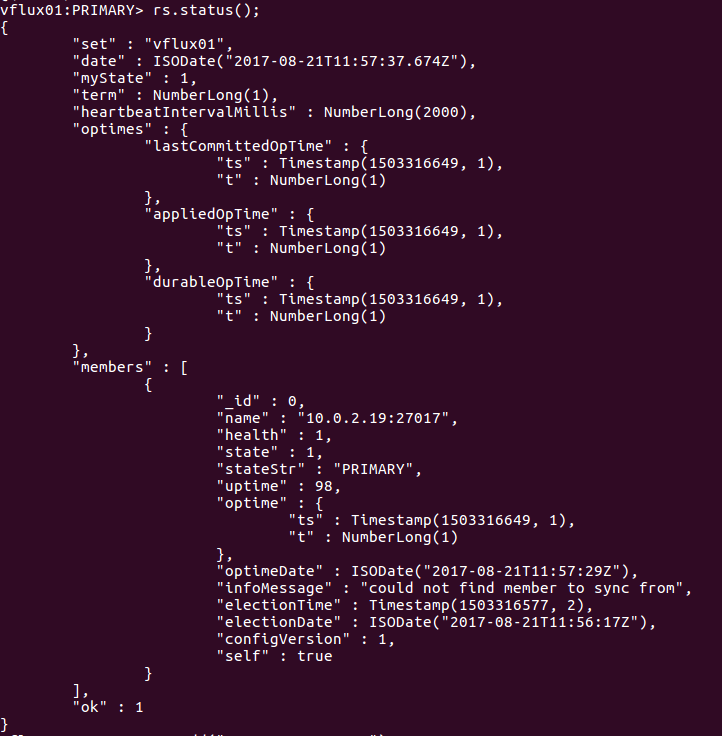
Figure 4. MongoDB Replicaset with Initial Member
Note that there is just one member with ip configured using rs.initiate command.
Add members to the replica set
Add other two members of the replica set by executing following command:
rs.add("ip_address_other_mongo_instance_1:27017");
Execute following command to check the replication status. Note one additional member added to the replica set.
rs.status()
Validate that replication works
- Create a collection in the primary server (write). Insert a couple of documents in this collection.
- Login into another member. You would note the SECONDARY prompt in mongo shell.
- Execute following command in order to read the data from SECONDARY or slave.
rs.slaveOk();
Above command allows the current connection to allow read operations to run on secondary members.
- Switch over to the collection and note that the collection is added and documents have been added.
- The Watermelon Effect: When Green Metrics Lie - January 25, 2026
- Coefficient of Variation in Regression Modelling: Example - November 9, 2025
- Chunking Strategies for RAG with Examples - November 2, 2025

I found it very helpful. However the differences are not too understandable for me